1.What is Dropshipping?
With the rapid development of cross-border e-commerce, new business models have emerged, among which dropshipping has become a popular choice for many entrepreneurs and small e-commerce sellers. So, what is dropshipping? How does it differ from the traditional inventory model? And what is its operational process? This article will answer these questions for you.
2.The Concept of Dropshipping
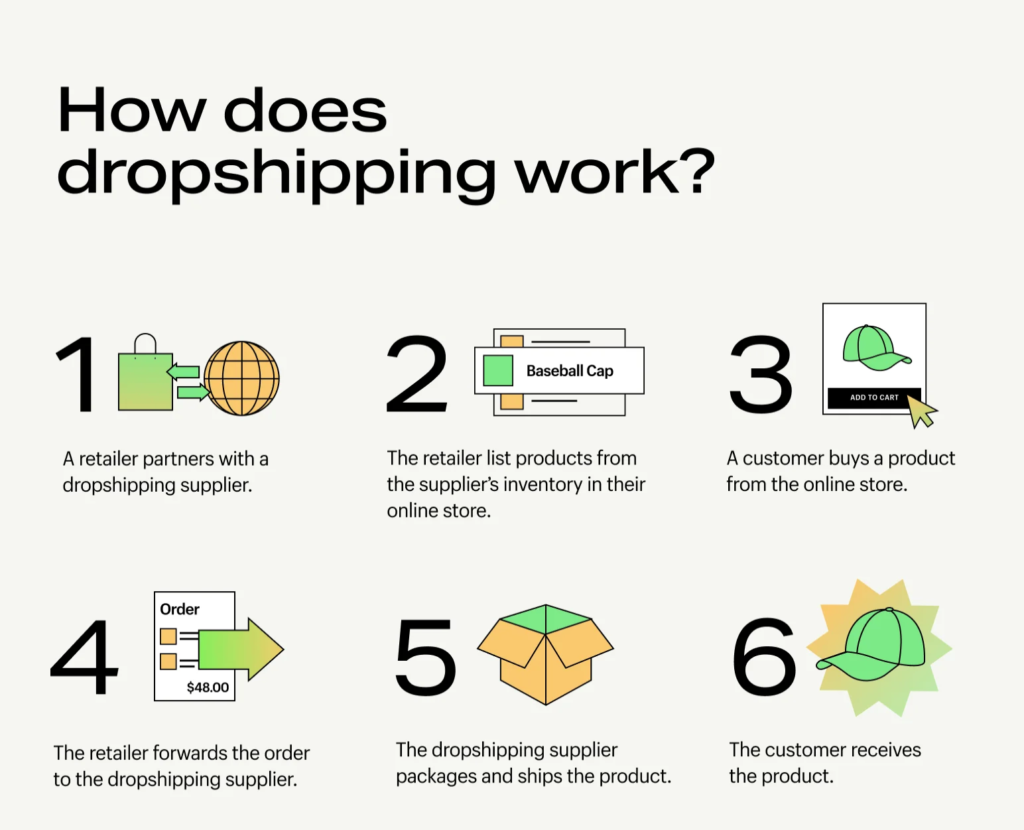
Dropshipping is an e-commerce logistics model where sellers do not need to purchase or hold inventory in advance. Instead, they collaborate with suppliers who ship products directly from their warehouses to the end consumers.
When a consumer places an order on the seller’s website or platform, the seller forwards the order information to the supplier, who is responsible for packaging and shipping the product.
Many entrepreneurs favor dropshipping because it delegates the responsibility of order fulfillment to the suppliers. This approach allows stores to avoid the costs of warehousing and the risk of unsold stock. Consequently, businesses can focus more resources on other aspects of retail, such as marketing.
3.Differences from the Traditional Inventory Model
| Comparison Item | Traditional Inventory Model | Dropshipping |
| Inventory Management | Sellers need to purchase products in advance and store them in their own warehouses, bearing the risk of overstock and storage costs. | Sellers do not need to hold inventory; products are shipped directly by the supplier, reducing financial pressure and inventory risk |
| Capital Investment | Requires a large amount of upfront capital to purchase products. | Requires less upfront capital, as sellers only pay suppliers after receiving orders from consumers. |
| Logistics Management | Sellers are responsible for the entire logistics process, including packaging, shipping, and after-sales service. | Suppliers handle logistics, including product packaging and delivery, simplifying the seller’s operational process. |
| Product Variety | Due to financial and storage constraints, sellers usually limit product variety. | Sellers can offer a wider range of products since they do not need to purchase inventory in advance. |
4.Operational Process of Dropshipping
- Choosing Suppliers:
Sellers need to find reliable suppliers to ensure product quality and timely delivery. When selecting suppliers, they can assess their reputation, product quality, and service capabilities. - Listing Products:
Sellers list products on their e-commerce platforms or websites and set appropriate prices. Product information is usually provided by the supplier, including images, descriptions, and specifications. - Order Processing:
When a consumer places an order, the seller forwards the order information to the supplier. This is typically done through an API interface or manual entry. - Supplier Shipping:
The supplier packages and ships the product based on the order information. Sellers can track the order’s logistics status in real time through the system. - After-Sales Service:
Sellers need to handle consumer after-sales issues, including returns, exchanges, and customer inquiries. Although the supplier ships the product, after-sales service is still the responsibility of the seller.
5.Conclusion
As a flexible business model, dropshipping provides sellers with lower financial barriers and higher operational efficiency. However, sellers need to be particularly cautious when choosing suppliers to ensure product quality and customer satisfaction. Through dropshipping, sellers can focus on marketing and customer service while leaving the complexities of logistics and inventory management to suppliers.
Hope this article helps you better understand dropshipping and make informed decisions in your cross-border e-commerce business!


